
Secretory granules
These pancreatic cells are arranged in spheres called acini or alveoli. In this example, the secretory granules contain digestive enzymes. These granules eventually fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing their contents by exocytosis into the acinar lumen. The base of each cell has abundant RER. The restricted apical distribution of the granules and the basally-located RER in these cells, is an example of cell polarity, a feature commonly seen in exocrine glands. Exocrine pancreas 1000x.
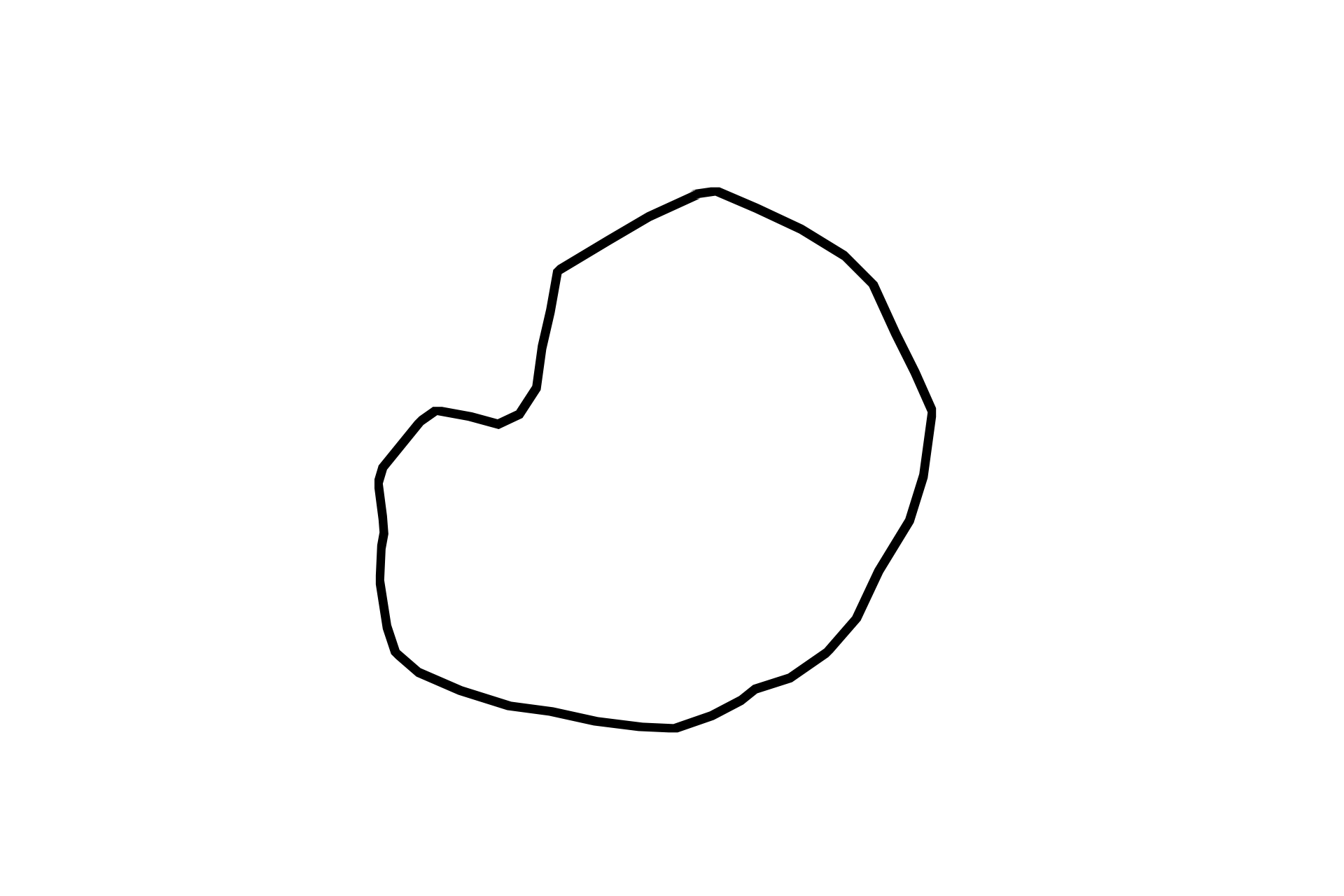
Acinus (alveolus)
These pancreatic cells are arranged in spheres called acini or alveoli. In this example, the secretory granules contain digestive enzymes. These granules eventually fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing their contents by exocytosis into the acinar lumen. The base of each cell has abundant RER. The restricted apical distribution of the granules and the basally-located RER in these cells, is an example of cell polarity, a feature commonly seen in exocrine glands. Exocrine pancreas 1000x.
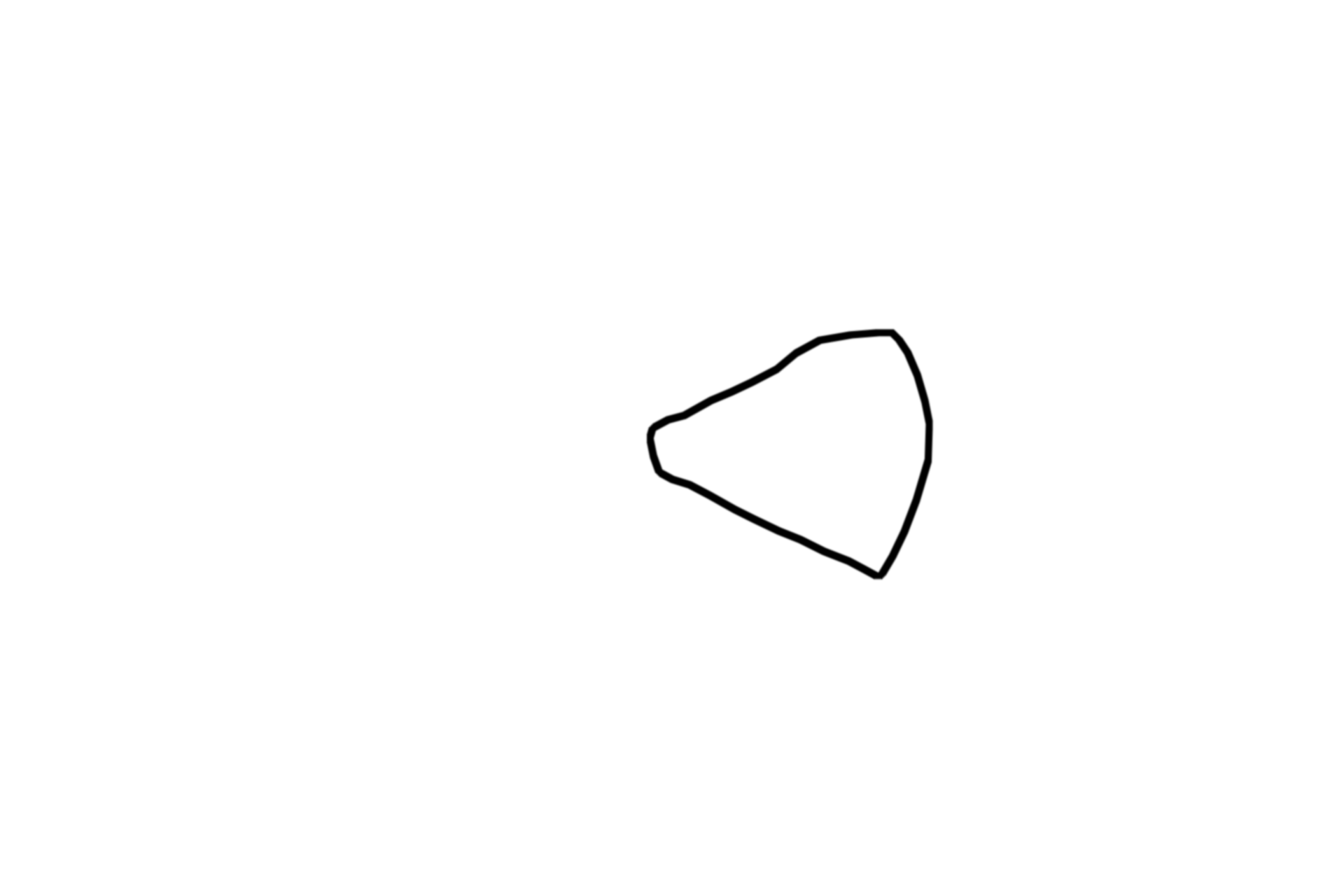
- Acinar cell
These pancreatic cells are arranged in spheres called acini or alveoli. In this example, the secretory granules contain digestive enzymes. These granules eventually fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing their contents by exocytosis into the acinar lumen. The base of each cell has abundant RER. The restricted apical distribution of the granules and the basally-located RER in these cells, is an example of cell polarity, a feature commonly seen in exocrine glands. Exocrine pancreas 1000x.
-- Secretory granules
These pancreatic cells are arranged in spheres called acini or alveoli. In this example, the secretory granules contain digestive enzymes. These granules eventually fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing their contents by exocytosis into the acinar lumen. The base of each cell has abundant RER. The restricted apical distribution of the granules and the basally-located RER in these cells, is an example of cell polarity, a feature commonly seen in exocrine glands. Exocrine pancreas 1000x.
-- RER
These pancreatic cells are arranged in spheres called acini or alveoli. In this example, the secretory granules contain digestive enzymes. These granules eventually fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing their contents by exocytosis into the acinar lumen. The base of each cell has abundant RER. The restricted apical distribution of the granules and the basally-located RER in these cells, is an example of cell polarity, a feature commonly seen in exocrine glands. Exocrine pancreas 1000x.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS