
Overview: Cranial nerve VIII
Cranial nerve VIII, the vestibulocochlear, innervates the receptors in the membranous labyrinth. The cochlear division of the nerve supplies the organ of Corti in the cochlear duct. The vestibular division supplies the macula in the utricle and in the saccule, as well as the crista ampullaris in the ampulla of each of the three semicircular ducts.

Cochlear division
Cranial nerve VIII, the vestibulocochlear, innervates the receptors in the membranous labyrinth. The cochlear division of the nerve supplies the organ of Corti in the cochlear duct. The vestibular division supplies the macula in the utricle and in the saccule, as well as the crista ampullaris in the ampulla of each of the three semicircular ducts.

Vestibular division
Cranial nerve VIII, the vestibulocochlear, innervates the receptors in the membranous labyrinth. The cochlear division of the nerve supplies the organ of Corti in the cochlear duct. The vestibular division supplies the macula in the utricle and in the saccule, as well as the crista ampullaris in the ampulla of each of the three semicircular ducts.
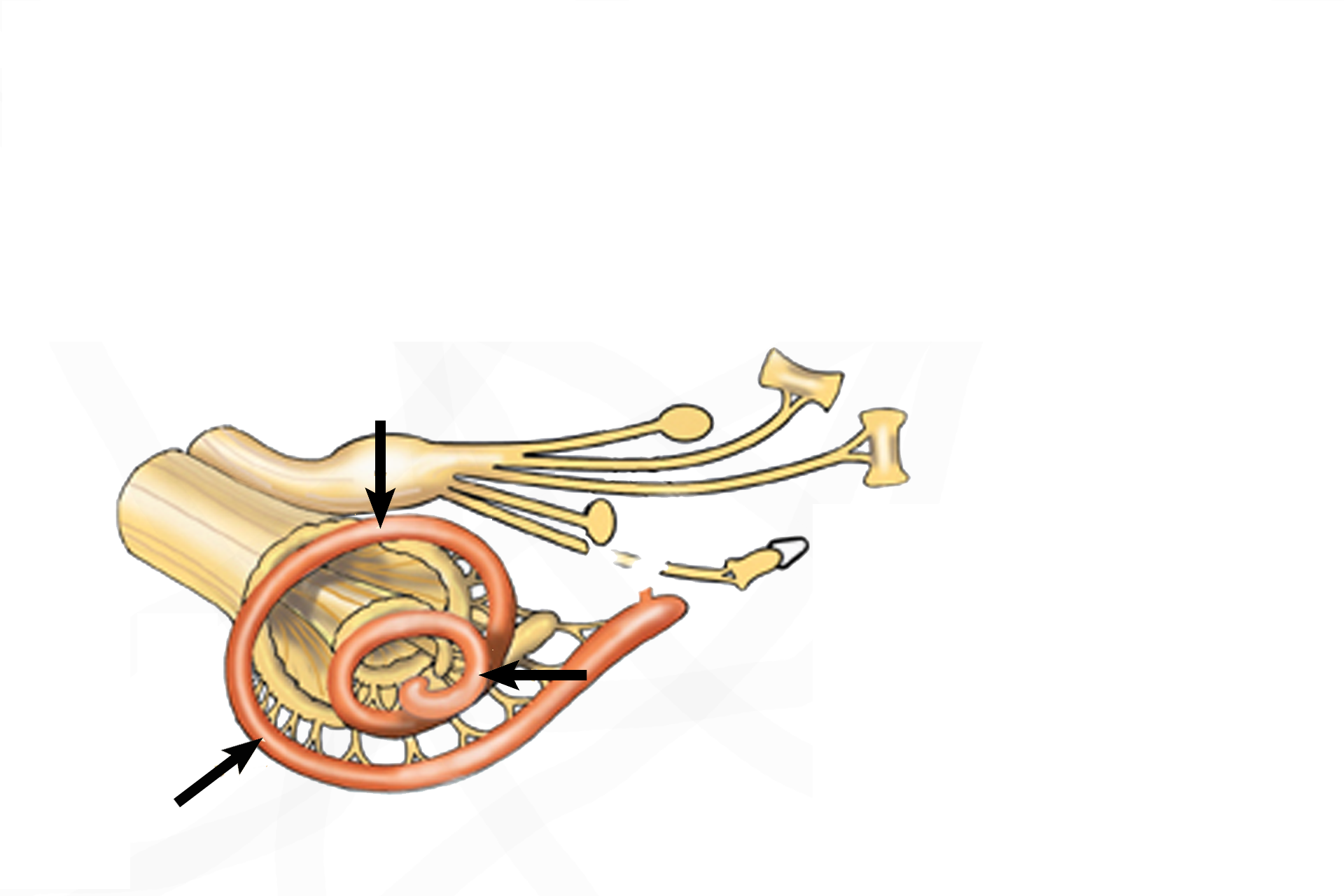
Organ of Corti >
The organ of Corti, the receptor for sound, is located in the cochlear duct (arrows) of the membranous labyrinth. The cochlear duct is suspended in the middle of the tubular osseous cochlea.
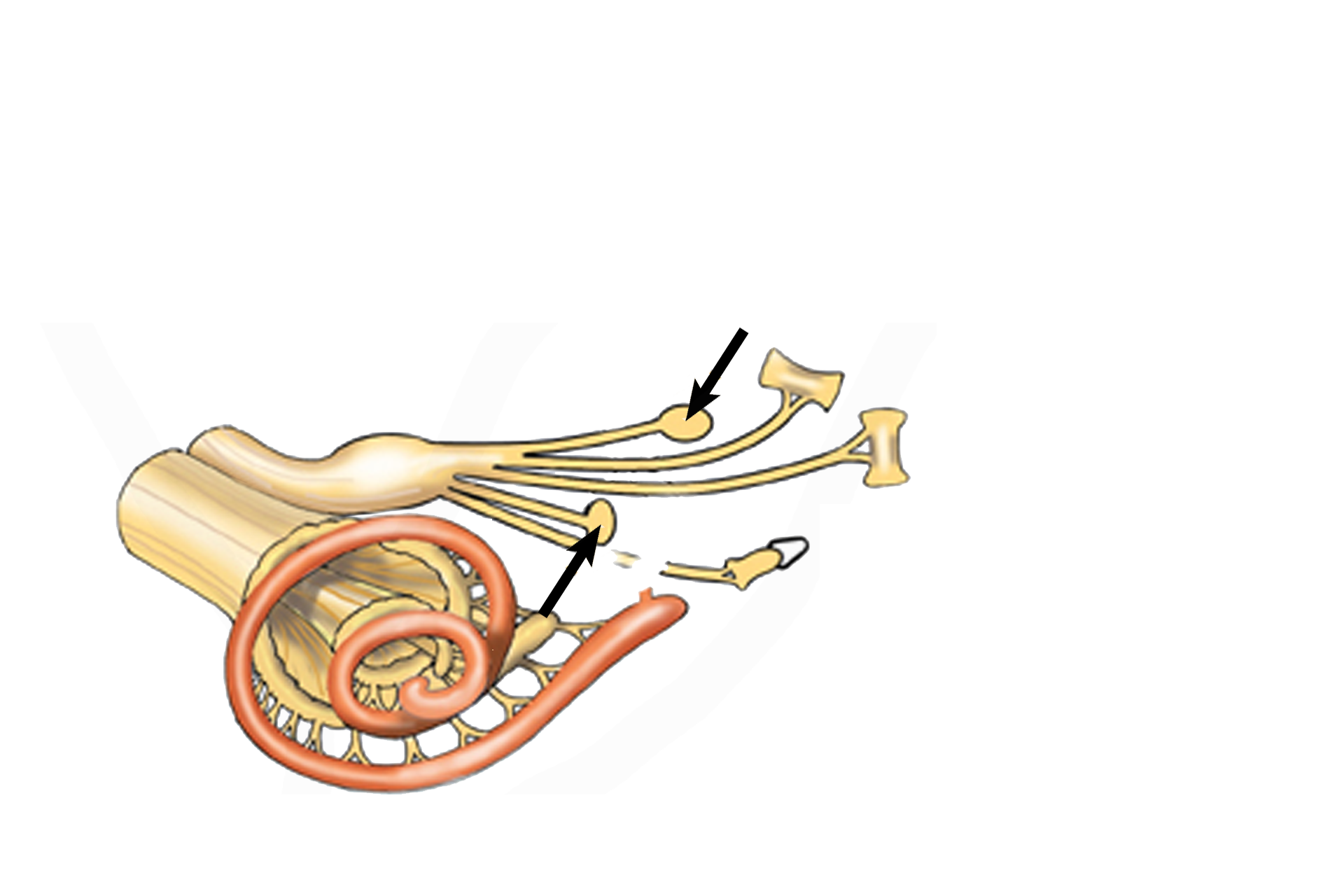
Maculae >
The receptor called the macula is a thickening in the wall of both the utricle and the saccule that responds to changes in linear acceleration and the force of gravity.
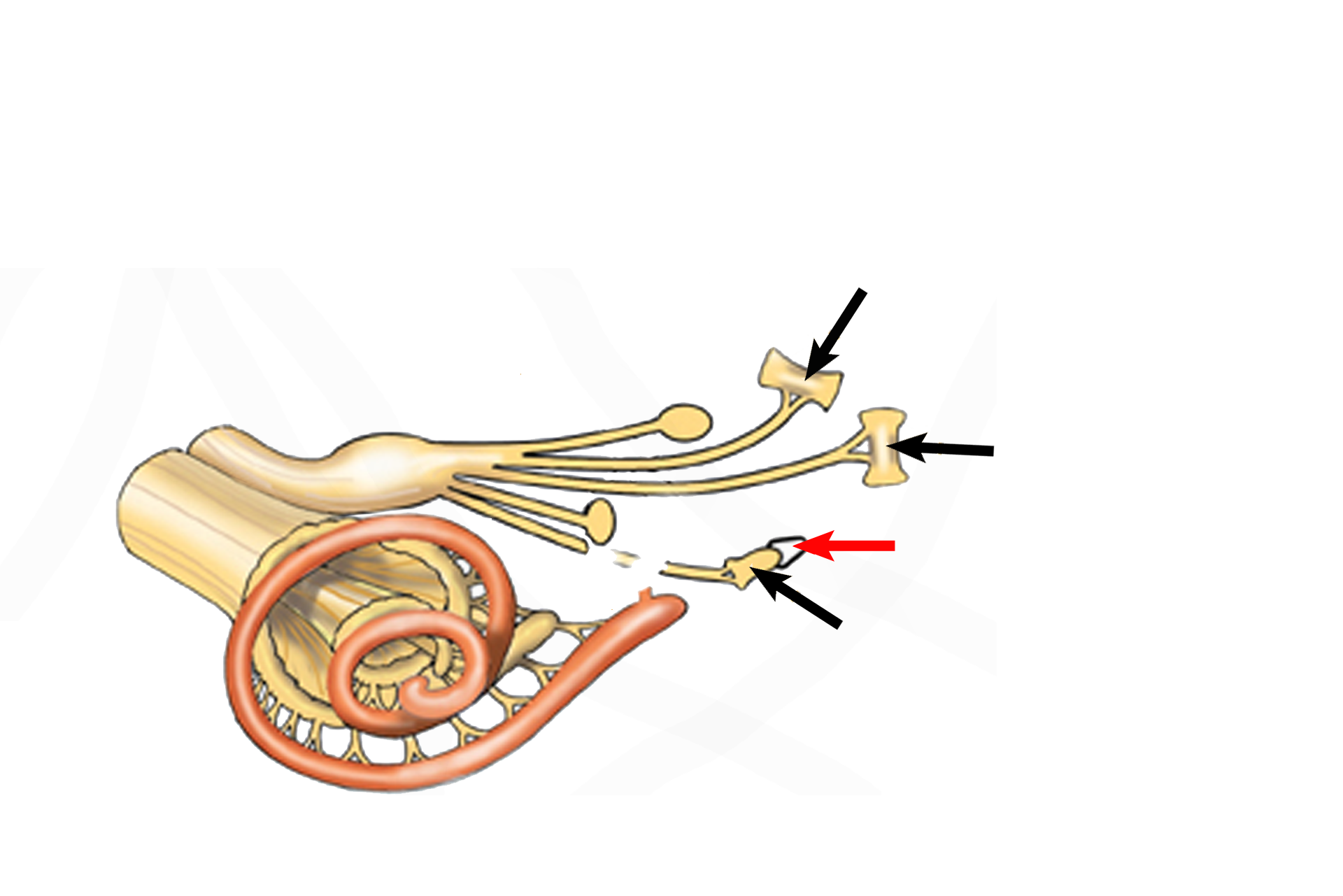
Cristae ampullares >
The receptor called the crista ampullaris (black arrows) is a ridge-like structure located in the ampullary enlargement of each semicircular duct. A gelatinous cupula (red arrow) extends from each crista to the opposite wall of the ampulla. Each crista lies perpendicular to the long axis of each duct and responds to angular acceleration.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS