
Overview
The drawing illustrates the internal organs of the female reproductive system: paired ovaries, paired oviducts (Fallopian tubes), uterus and vagina.
Ovaries >
The paired ovaries ovulate a female germ cell (exocrine function) approximately once each month. The endocrine function of the ovary is the secretion of the hormone estrogen during the first half of the ovarian cycle and the hormones progesterone and estrogen during the second half. These hormones regulate the activity of the other organs of the female reproductive system.
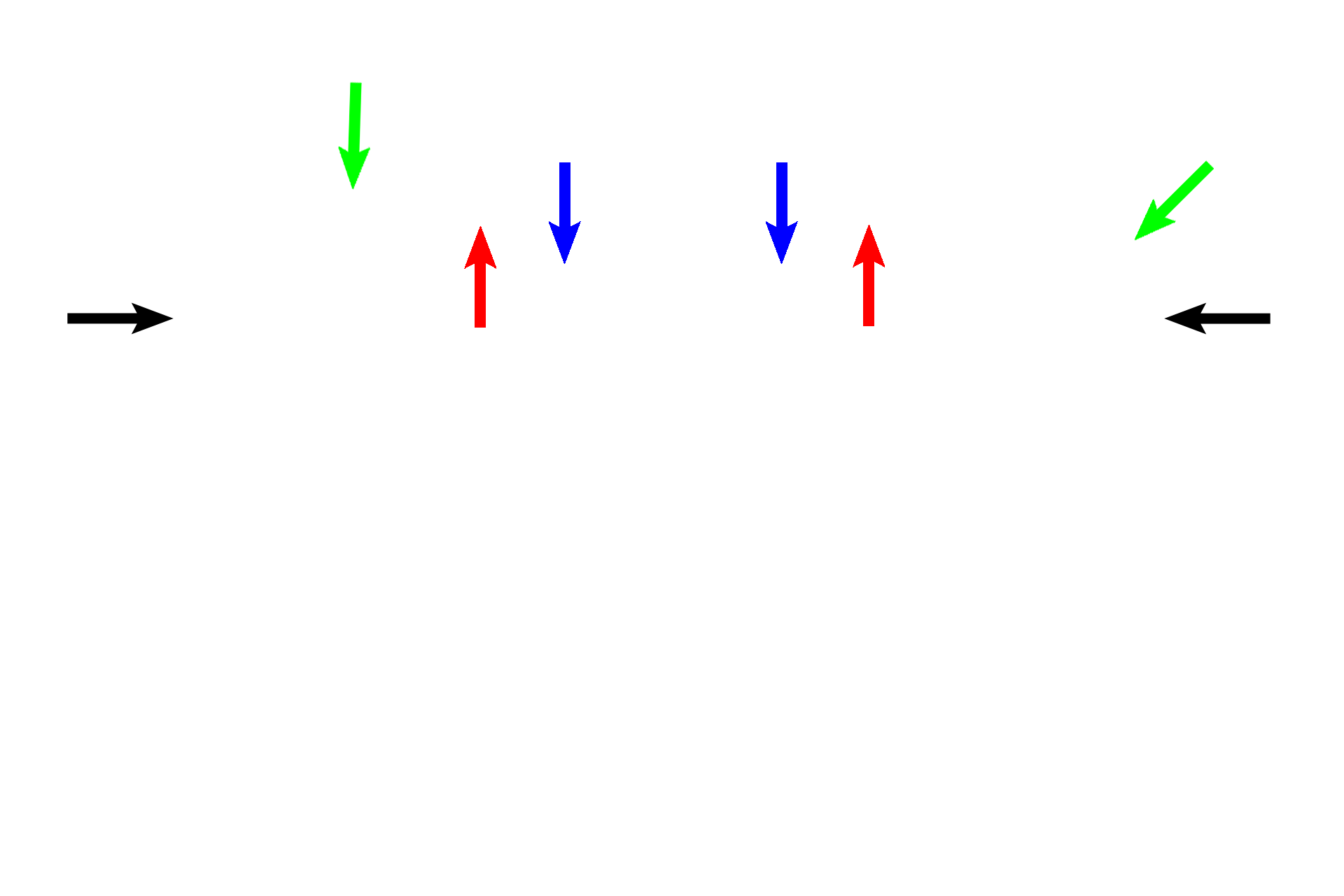
Oviducts >
Each oviduct (Fallopian tube) interconnects the ovary and the uterus and is divided into four segments: infundibulum (black), ampulla (green), isthmus (red) and intramural (blue) portions. The ampulla, near its junction with the isthmus, serves as the site of fertilization. The oviducts, therefore, transport sperm and oocyte to the site of fertilization and transport the embryo from this site into the uterus.
Uterus >
The embryo implants into the uterus about day 21 of the menstrual cycle. The mucosal lining (endometrium) of the uterus forms the maternal portion of the placenta that surrounds and nourishes the embryo/fetus for the 40 weeks of pregnancy. The smooth muscle of the uterus expels the fetus at parturition.
- Fundus >
The fundus of the uterus extends above the opening of the oviducts. The body forms the main mass of the uterus. The isthmus is the narrowing between the body and the cervix. The most inferior portion of the uterus, the cervix, projects into the vagina.
- Body
The fundus of the uterus extends above the opening of the oviducts. The body forms the main mass of the uterus. The isthmus is the narrowing between the body and the cervix. The most inferior portion of the uterus, the cervix, projects into the vagina.
- Isthmus
The fundus of the uterus extends above the opening of the oviducts. The body forms the main mass of the uterus. The isthmus is the narrowing between the body and the cervix. The most inferior portion of the uterus, the cervix, projects into the vagina.
- Cervix
The fundus of the uterus extends above the opening of the oviducts. The body forms the main mass of the uterus. The isthmus is the narrowing between the body and the cervix. The most inferior portion of the uterus, the cervix, projects into the vagina.
Vagina >
The vagina serves as the depository for sperm and forms part of the birth canal at parturition.
