
Jejunum or ileum
The jejunum and ileum (shown here) can be differentiated from the duodenum, primarily by the lack of glands in the submucosa. Villi of the small intestine possess a lacteal that transports absorbed lipids to lymphatic vessels in the submucosa. A plica circularis, a circular fold of submucosa and its overlying mucosa, is centrally located in the image. Trichrome stain, 40x
Mucosa
The jejunum and ileum (shown here) can be differentiated from the duodenum, primarily by the lack of glands in the submucosa. Villi of the small intestine possess a lacteal that transports absorbed lipids to lymphatic vessels in the submucosa. A plica circularis, a circular fold of submucosa and its overlying mucosa, is centrally located in the image. Trichrome stain, 40x
- Villi
The jejunum and ileum (shown here) can be differentiated from the duodenum, primarily by the lack of glands in the submucosa. Villi of the small intestine possess a lacteal that transports absorbed lipids to lymphatic vessels in the submucosa. A plica circularis, a circular fold of submucosa and its overlying mucosa, is centrally located in the image. Trichrome stain, 40x
- Intestinal glands
The jejunum and ileum (shown here) can be differentiated from the duodenum, primarily by the lack of glands in the submucosa. Villi of the small intestine possess a lacteal that transports absorbed lipids to lymphatic vessels in the submucosa. A plica circularis, a circular fold of submucosa and its overlying mucosa, is centrally located in the image. Trichrome stain, 40x
- Lamina propria
The jejunum and ileum (shown here) can be differentiated from the duodenum, primarily by the lack of glands in the submucosa. Villi of the small intestine possess a lacteal that transports absorbed lipids to lymphatic vessels in the submucosa. A plica circularis, a circular fold of submucosa and its overlying mucosa, is centrally located in the image. Trichrome stain, 40x
- Lacteals
The jejunum and ileum (shown here) can be differentiated from the duodenum, primarily by the lack of glands in the submucosa. Villi of the small intestine possess a lacteal that transports absorbed lipids to lymphatic vessels in the submucosa. A plica circularis, a circular fold of submucosa and its overlying mucosa, is centrally located in the image. Trichrome stain, 40x

Submucosa
The jejunum and ileum (shown here) can be differentiated from the duodenum, primarily by the lack of glands in the submucosa. Villi of the small intestine possess a lacteal that transports absorbed lipids to lymphatic vessels in the submucosa. A plica circularis, a circular fold of submucosa and its overlying mucosa, is centrally located in the image. Trichrome stain, 40x
- Plica circularis
The jejunum and ileum (shown here) can be differentiated from the duodenum, primarily by the lack of glands in the submucosa. Villi of the small intestine possess a lacteal that transports absorbed lipids to lymphatic vessels in the submucosa. A plica circularis, a circular fold of submucosa and its overlying mucosa, is centrally located in the image. Trichrome stain, 40x
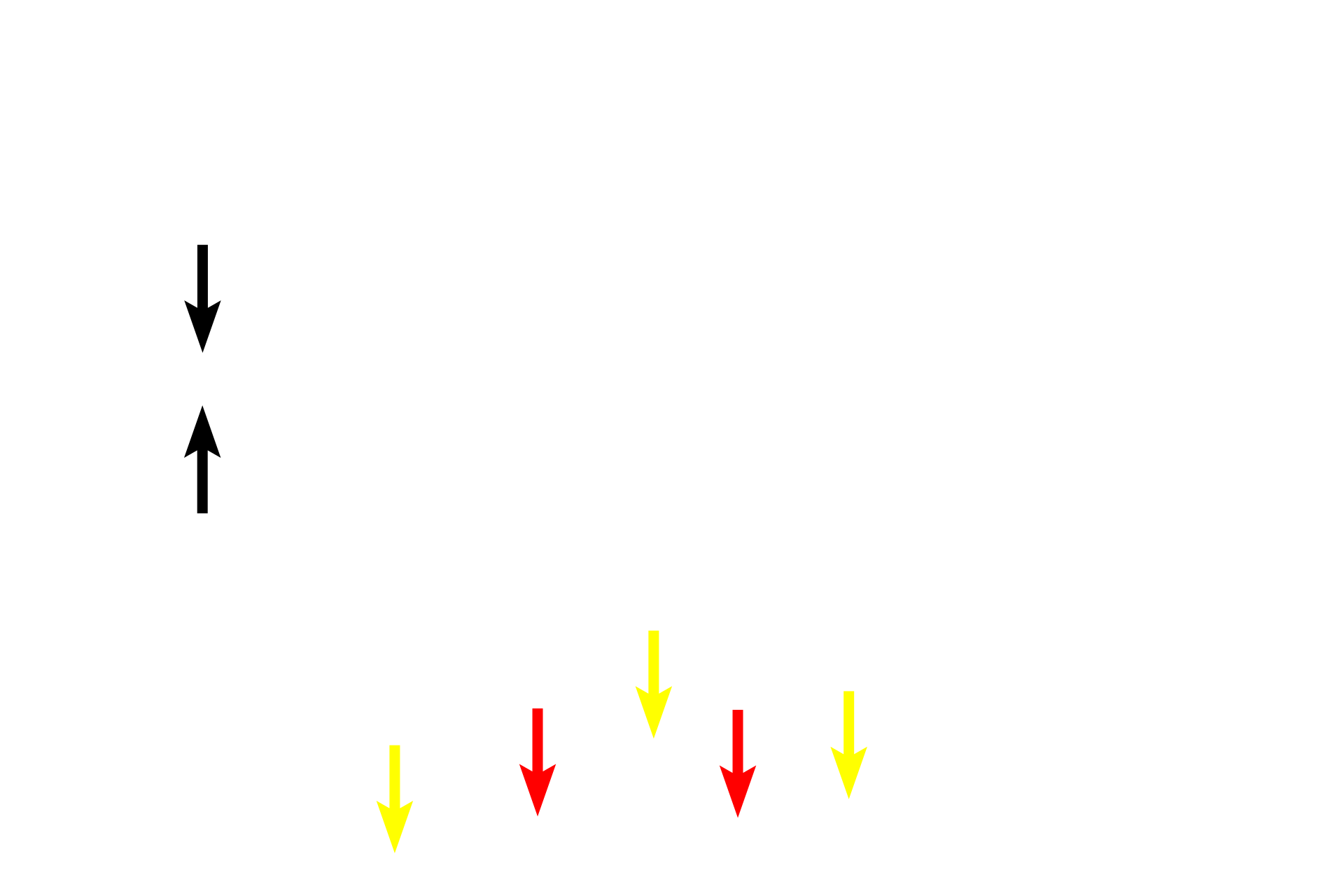
Muscularis externa >
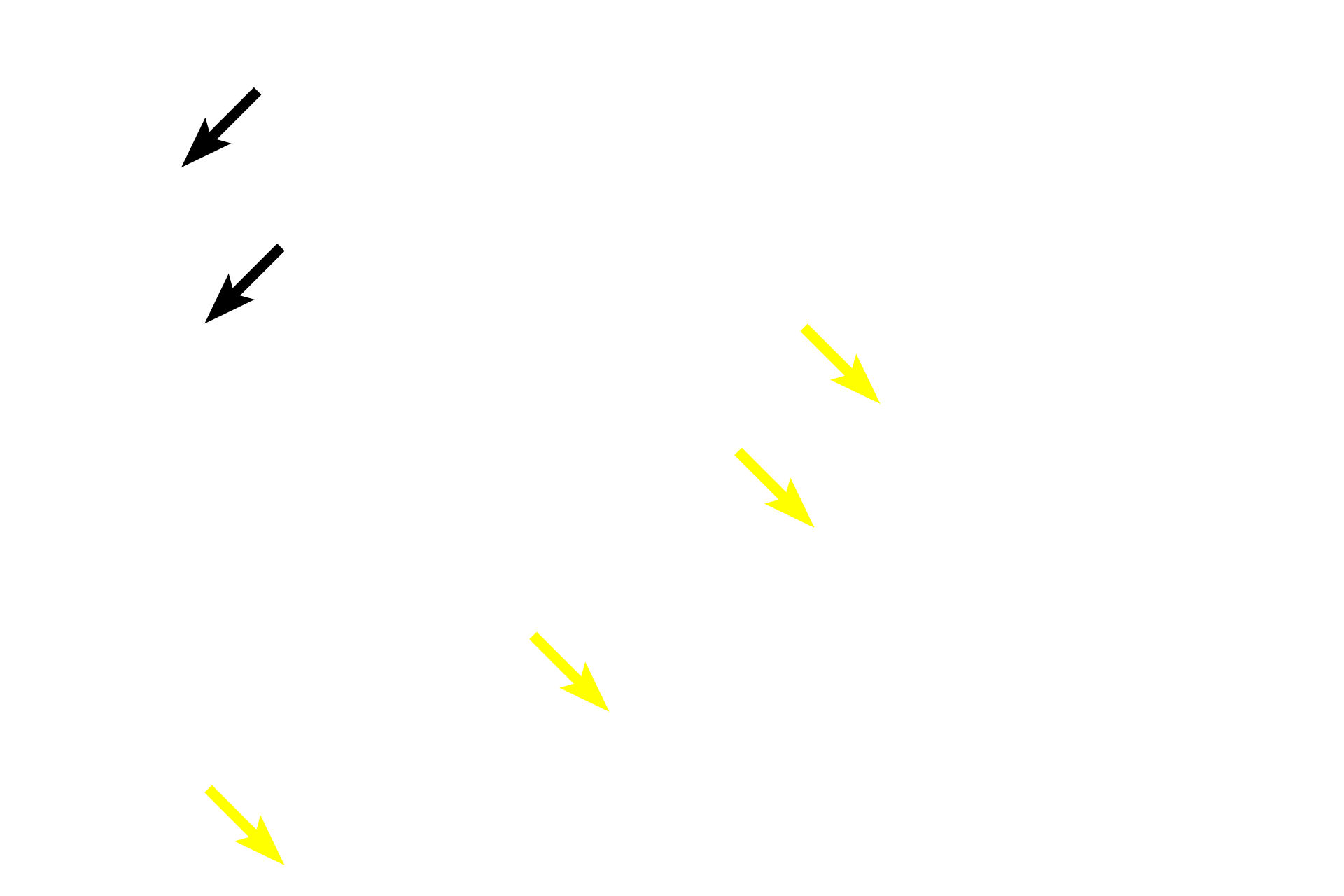
In this longitudinal section, the muscle fibers in the inner circular layer of the muscularis externa are cut in cross section (yellow arrows); fibers in outer longitudinal layer of the muscularis externa are cut lengthwise (red arrows). The myenteric plexus (Auerbach’s plexus) is located between these layers of smooth muscle.
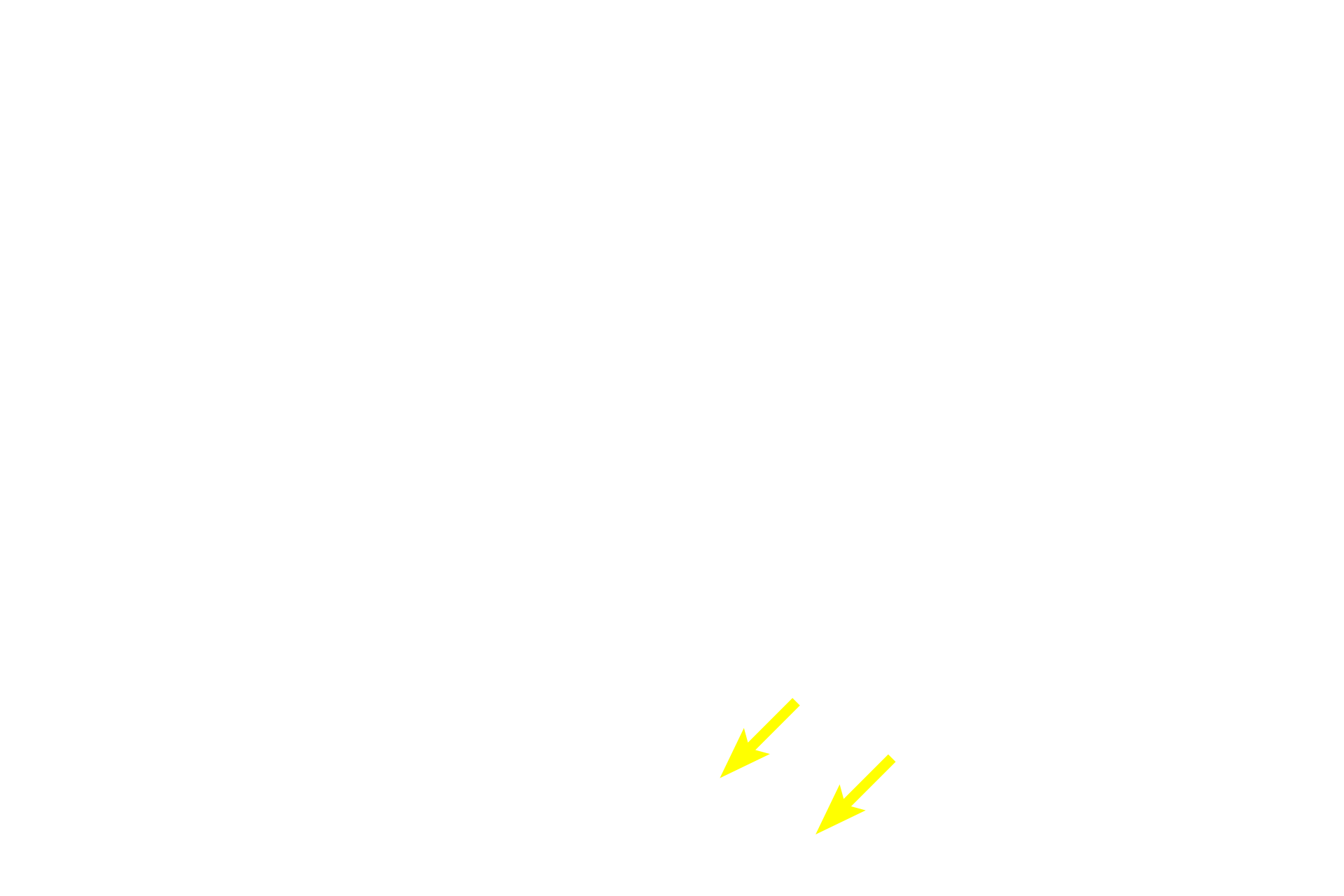

- Myenteric plexus (Auerbach’s plexus)
In this longitudinal section, the muscle fibers in the inner circular layer of the muscularis externa are cut in cross section (yellow arrows); fibers in outer longitudinal layer of the muscularis externa are cut lengthwise (red arrows). The myenteric plexus (Auerbach’s plexus) is located between these layers of smooth muscle.